Paedodontics
Overview
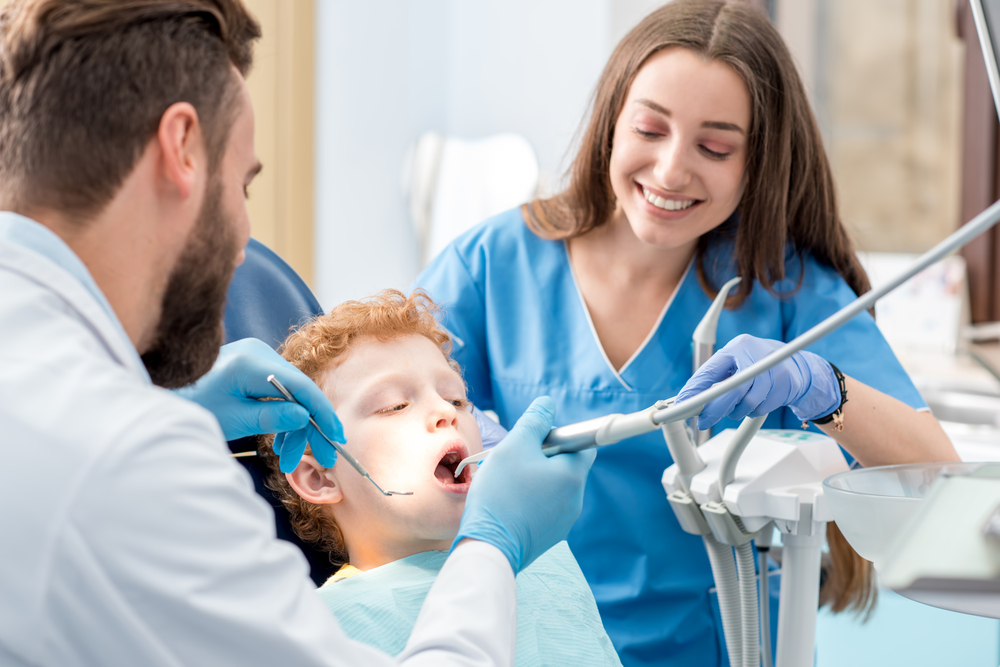
Pedodontics: (Pediatric Dentistry) is based on the healthy preservation of the milk and permanent teeth of children and teenagers in the 0-18 age group. It is a branch of dentistry that aims to eliminate the problems caused by caries, trauma, hereditary and similar factors in these teeth.
Pedodontics is a branch of dentistry, that follows and treats the oral-dental health and chin and face development of children from childhood, and also includes preventive measures. In this period, pedodontists perform all kinds of preventive and curative treatments and preventive applications according to the oral and dental health needs of babies, children and young people.
Applied Treatments:
- Oral and Dental Care and Nutrition Recommendations for Mother and Child
- Child Dentures and Crowns (Stainless Steel Crowns, Zirconium Crowns)
- Tooth Extraction
- Protective and Preventive Applications from Tooth Decay
- Treatment of Dental Traumas
- Endodontic Treatments (Root Canal Treatments)
- Treatments to Stop Bad Mouth Habits (Finger Sucking, Nail Biting, Lip Biting, etc.)
- In Primary and Young Permanent Teeth: Placeholders for Early Loss of Primary Teeth
- In Primary and Young Permanent Teeth: Restorative Treatments (Fillings)
A healthy smile begins with a child.
Why Are Milk Teeth
Important?
There are 20 milk teeth in total. It starts to erupt at the age of 4-6 months and leaves its place to permanent teeth by the age of 5-8 years. The most important task of milk teeth is to provide nutrition to the child. In addition, the proper development of speech also depends on the presence of milk teeth. Milk teeth protect the area they cover for the permanent tooth that will replace them and guide it while the permanent tooth is erupting. When the primary tooth is pulled out early, this natural place-holding function also disappears, and then it causes loss of space in the jaw. This loss of space leads to problems such as crowding in the permanent teeth that will last. For this reason, until the eruption of the permanent teeth is completed (11-13 years), the deciduous teeth should remain in the oral environment. Early lost milk teeth also negatively affect the jaw and facial development of children who are at the age of growth and development. In addition, nutritional problems in children cause psychological and self-confidence problems.
How Are Paedodontics Treatment
Methods Performed?
What are preventive treatments?
The primary aim of pediatric dentistry is to take measures to prevent dental problems and to direct children to a caries-free future. The procedures applied for this purpose are called Preventive Dentistry Practices. For preventive applications to prevent dental caries, great importance is attached to educating the child and his family about oral and dental health and nutrition. Fluoride applications and fissure sealant procedures are among the preventive dentistry applications.
What are Fissure Sealers and What Do They Do?
It is a fluid filling material that closes the deep and decay-prone fissures (grooves) on the chewing surfaces of permanent teeth and does not allow bacteria to reach there, thus preventing caries. In teeth with fissure sealant applied, these deep grooves that the brush cannot reach become a brushable surface. It has been proven that the bacterial uptake in fissure sealant applied teeth is reduced by an average of 100 times. Fissure sealant applications should be checked every 6 months.
What is Fluorine Application?
Fluorine is an element that prevents tooth decay and strengthens the structure of teeth. Since the enamel is not fully mature when the teeth first erupt, newly erupted teeth are generally less resistant to caries and are prone to caries formation. Fluoride strengthens the enamel, protects the tooth against acid attacks and thus helps prevent the formation of dental caries. Professional superficial fluoride application is a protective method that can only be applied by dentists. Superficial fluor should be applied by a dentist every 6 months.
What is a Placeholder?
By some children, loss of milk teeth may occur due to caries, infection, dental trauma or genetic problems.Tooth loss that occurs outside of pre-age conditions is described as early tooth loss. Placeholders are put in their place.These placeholders prevent tooth crowding and ensure that the next teeth take their place in a healthy way. At the same time, it prevents the adjacent teeth from leaning towards the spaces.
Treatment with General Anesthesia and Sedation:
Treatment under general anesthesia is offered to patients who are very young and/or who are unable to act cooperatively despite the use of behavioral stimulation techniques during regular treatment, or to patients with mental/physical disabilities. These operations are performed in an environment where anesthesia is administered by a doctor and his team specialized in anesthesiology. Under general anesthesia, all necessary preventive, treatment and extraction procedures, including the placement of placeholders for primary teeth that need to be extracted early, are performed in one go. This treatment, performed under general anesthesia, provides a complete oral rehabilitation followed by periodic check-ups.
ISMAN Dental Clinic Services
Get In Touch With Us
Schedule an interview to get a free quote, simply fill out the form below and we will contact you back regarding the intervention you require.
Teething is a physiological process that all children experience. Teething and Symptoms Most children begin erupting their first tooth at about six months of age and have completed 20 primary teeth by 30 months. The milk teeth begin to appear in a certain order in the mouth, and this process is called the “milk dentition period”. This finding indicates that the deciduous teeth are preparing to erupt by piercing the gums. Dry cough, whining, sleep disturbance, gum inflammation, drooling are among the most common symptoms during the eruption of milk teeth. However, fever, diarrhea and numerous other complaints are commonly cited as problems with the teething process, despite the lack of sufficient evidence. Initial signs of teething include increased drooling, restlessness, and localized discomfort in the area of
Applications in the Teething Process: The teething process is a concern for most parents. It is stated that gum pain associated with teething can be reduced by using a wet wash cloth or cold tooth rings, or by massaging the gums with a clean finger. It is emphasized that during this process, families massage their babies’ gums with a clean and cold cloth, apply dental gels before feeding, give teethers to massage the gums or give them something to chew (carrot…) reduces the pain and restlessness of babies and helps them to pass this process more comfortably. . The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) recommends the application of chilled rings and oral analgesics to the gums of infants for the treatment of symptoms. The AAPD does not recommend the use of topical anesthetics, including over-the-counter dental gels, for relief due to the strong toxicity of these products. Conservative use of acetaminophen and ibuprofen can help relieve teething pain. Gel containing benzocaine are not recommended for infants due the risk of methemoglobinemia.
Oral and dental care starts with the first tooth. Teeth care in babies should be started before the teeth erupt, and all teeth should not be expected to come out. Parents have great responsibilities in starting the oral cleaning of the little ones. The World Association of Pediatric Dentists states that newborn babies should be cleaned after each feeding. Even before baby teeth erupt, it can be wiped softly with a clean damp gauze after feeding. As the baby grows, there is a transition towards using a baby toothbrush for cleaning. The baby who brushes teeth, on the one hand, acquires the necessary habit for dental care at a young age, on the other hand, it prevents the decay of milk teeth.
